How To Change Gas Price and Gas Limit In Crypto Transactions
Using Cwallet to conduct transactions automatically adjusts the gas limit to the exact amount required for the transaction to pass through and nothing more, so you don't pay more than necessary.

Transactions in the cryptocurrency market entail more than just sending and receiving digital assets. You also need to understand the complexities of gas prices and gas limit modifications are critical for guaranteeing the seamless execution of your blockchain transactions.
Gas is the "fuel" that powers the execution of transactions and smart contracts on blockchain networks such as Ethereum. You start a sequence of computations when you send cryptocurrency or interact with smart contracts. Each step requires a certain amount of computational power, which is quantified in units called "gas."
As you use online wallets like Cwallet, comprehending gas prices and gas limit adjustments is akin to knowing how much fuel your car requires for a journey. Gas price determines the speed at which your transaction is processed, while the gas limit dictates your transaction's complexity and potential resource consumption. Without a clear understanding of these concepts, you may end up with transactions that take longer than expected or fail to complete altogether.
This article serves as a guide to help crypto traders navigate the complexities of gas fees, empowering them to make informed decisions and optimize their crypto transactions.
Gas Price: What is it and Why Does it Matter?
Gas price refers to the fee you're willing to pay for executing a cryptocurrency transaction on the blockchain. It's measured in a specific unit (e.g., Gwei in Ethereum) and represents the amount of cryptocurrency you're ready to spend per unit of computational work required to process your transaction.
Gas price is crucial in determining how quickly your transaction gets included in a block and confirmed by the network. Miners prioritize transactions with higher gas prices because they want to maximize their earnings. When you set a higher gas price, miners are more likely to include your transaction in the next block they mine, ensuring faster confirmation times.
Factors Influencing Gas Price Fluctuations
A variety of factors influences gas price fluctuations:
- Network Congestion: During times of high demand, such as when there's a popular ICO or a sudden surge in transactions, gas prices tend to increase as users compete to have their transactions processed quickly.
- Blockchain Activity: The activity level on the blockchain also affects gas prices. More complex transactions or interactions with smart contracts require higher gas prices to incentivize miners to process them.
- Market Speculation: Gas prices can also be influenced by market sentiment. If users expect the value of the cryptocurrency to increase significantly, they might be more willing to pay higher gas prices to ensure their transactions are processed promptly.
Gas Limit: What is it?
Gas limit refers to the maximum amount of computational work that a blockchain network will allow for a specific transaction. It's measured in units of gas, representing the computational effort required to process and validate the transaction on the network.
Consequences of Setting an Insufficient Gas Limit
- Transaction Failures: The transaction may fail if the gas limit set for a transaction is insufficient to cover the computational work needed. This failure can occur if the gas limit is too low to support the complexity of the transaction, causing the transaction to be rejected by the network.
- Stuck Transactions: Sometimes, a transaction might get stuck in a "pending" state if the set gas limit is close to the minimum requirement. The network may not have enough gas allocated to complete the transaction, leading to delays or indefinite stalling of the transaction's execution.
- Opportunity Cost: Setting an overly conservative gas limit could mean that your transaction takes longer to be processed, as miners might prioritize transactions with higher gas limits. This could lead to missed opportunities, especially during periods of network congestion when transaction confirmations become competitive.
- Smart Contract Issues: When dealing with smart contracts, an insufficient gas limit might cause the contract execution to halt unexpectedly. This can result in an incomplete or incorrect execution of the intended action within the smart contract.
Using Cwallet Can Help You With Minimal Gas Fees
Cwallet is a cryptocurrency wallet with various automatic functions that help you pay the least amount of gas costs possible. Using Cwallet to conduct transactions automatically adjusts the gas limit to the exact amount required for the transaction to pass through and nothing more, so you don't pay more than necessary. Even better, the wallet allows users within its network to transmit and receive crypto tokens and NFTs without incurring any gas fees.
Cwallet offers several transactions to ease crypto transactions. Signing up on Cwallet issues you a unique Cwallet ID that allows you to make gas-free transactions with other Cwallet users using their Cwallet ID.
Cwallet also has a non-custodial wallet option that allows you to manage your swap transactions automatically and calculate what’s the best for your trades.
From the default custodial wallet option, you can easily switch to the non-custodial wallet with a single click, as shwon below.
From the non-custodial wallet, you can easily swap tokens, and of course, with more freedom, including the ability to select gas prices and limits.
From the non-custodial wallet homepage, all you need to do is locate swap, at the bottom of the page
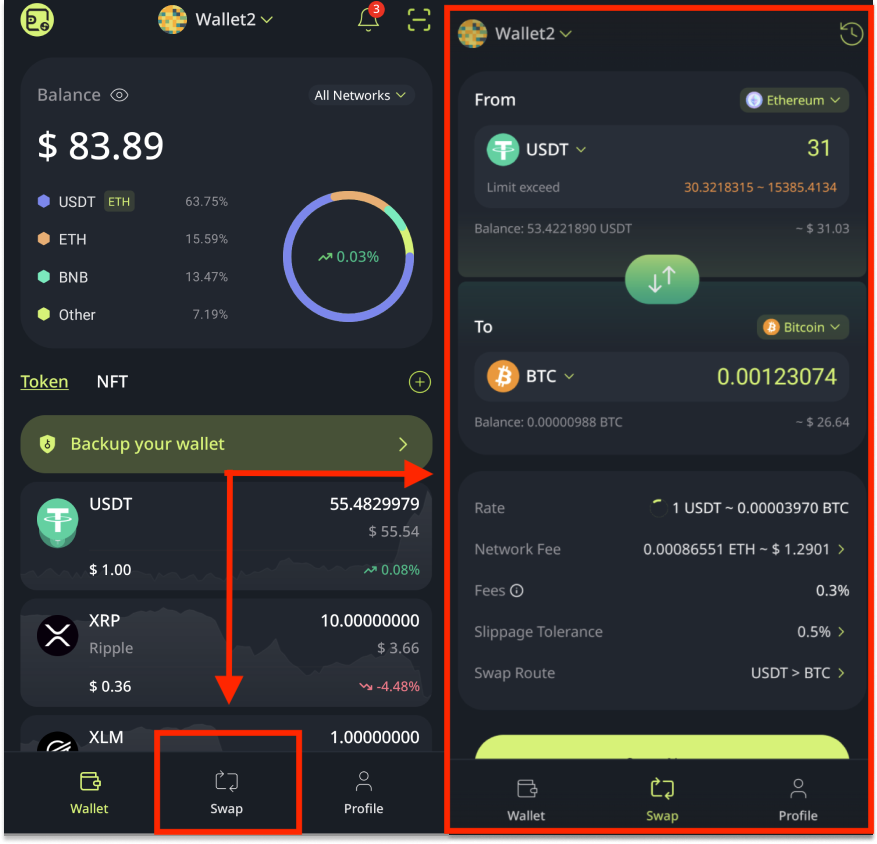
then;
- Choose the "From Token" and Network
- Then, choose the "To Token" and Network you want.
- Enter the amount of From Token, the amount you fill in has to be within the limitation to ensure the transaction can be created successfully.
- Then you can customize the network fee, slippage tolerance, and transaction route for cross-chain transactions, as shown below.
Conclusion
As a trader who wants to make the most profit, you should understand what gas fees are and understand it adequately. This would determine how much costs and profits you make while trading crypto.
Download Cwallet today and enjoy gas-free transactions.