Cryptocurrency And Blockchain For Beginners: The Ultimate Guide
You are probably reading this because you have heard of cryptocurrency and don’t fully grasp the concept! This user guide will explain everything you need to know to begin your cryptocurrency journey.
In this guide, you will learn about:
- The concept of Cryptocurrency and Blockchain
- Wallets, how to set up your first crypto wallet & securely back up your wallet
- How to send and receive assets using a crypto wallet
- Decentralized Applications (DApps)
- Smart Contracts
- DeFi security practices
- Crypto/Blockchain security practices
- Types of security attacks you should be wary of
- How to mitigate losses in the case of a security breach.
You are probably reading this because you have heard of cryptocurrency and don’t fully grasp the concept! Although the cryptocurrency industry is currently expanding rapidly, it is still in its infancy.
So, what is cryptocurrency? What advantages does it have for you? I know you're thinking about these questions, and you'd like to have them answered as quickly as possible. So, this user guide will explain everything you need to know.
Cryptocurrency eliminates centralization in our financial system. As a result, party A can make transactions with Party B without relying on banks, governments, or financial institutions.
In other words, we can define cryptocurrency as an ecosystem involving a network of digital payment systems that facilitates peer-to-peer transactions, allowing anyone to send and receive money without compromising security.
So, since there are no third parties involved, who/what verifies and secures these decentralized transactions?
ANSWER - THE BLOCKCHAIN.
What is Blockchain?

The Blockchain is a ledger, a record book that contains details of crypto transactions. These details include but are not limited to Sender’s address, receiver’s address, token spent, amount, timestamps, etc.
In other words, a blockchain is an accurate record of time-stamped transaction data.
So what makes the blockchain special?
Unlike traditional financial systems, the blockchain is not controlled by any central authority; instead, it is managed by a network of computers (nodes) scattered across the globe. Hence, no central entity can alter, falsify, or compromise data on the blockchain.
Blockchain data is public and visible to anyone - nothing is hidden; regardless of this transparency, blockchain data remains secure.
Blockchain helps to facilitate “trustlessness” in transactions. I’ll explain this with an example.
If I made a bank/wire transfer of $500 to you, you would need to trust me or give me the benefit of the doubt that I indeed sent the money. After a few hours, if you don’t get the money, you may reach out to me again to confirm that the transaction went through. You will have doubts until the money arrives in your account.
However, with the blockchain, as soon as I send the $500 to you, I need to send you the Transaction ID, from which you can publicly verify the transaction.
This trustlessness makes the blockchain an incredible innovation; it produces a financial system that cannot be manipulated when combined with cryptocurrency.
Let’s examine how to get you started in cryptocurrency so that you can set up your portfolio yourself.
Creating A Wallet
A crypto wallet is essential to your crypto journey; it is just like your traditional bank account, without which you can’t make any financial transactions.
Click here to read a detailed beginner explanation of what crypto wallets are
- Before downloading a wallet, deciding between a custodial or non-custodial wallet is essential.
- After deciding between a custodial or non-custodial wallet, you need to research before downloading any wallet.
- Google the wallet name and check for reviews
- Check social media, and see what people are saying
- Ask people you know personally for their reviews on these wallets
- Securely store your wallet’s mnemonic phrase if you select a noncustodial wallet to ensure that you don’t expose yourself to malicious attackers. Here is a detailed guide on securing your wallet’s seed phrase
Using A Wallet
A crypto wallet is a gateway for accessing several cryptocurrency services, particularly swapping, sending, and receiving crypto assets/tokens. In addition, non-custodial hot wallets are also used to access DeFi services (DEX, NFT, Blockchain games) via dApps.
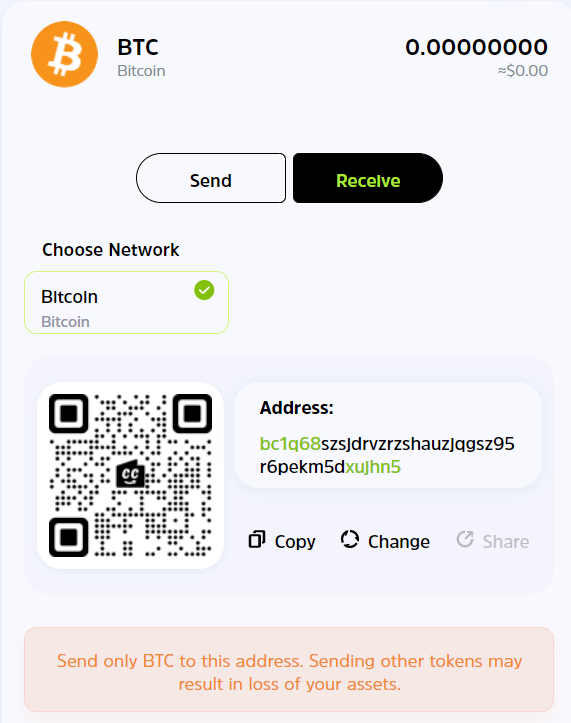
How to Receive a Crypto Asset
- Launch your wallet.
- Search for the token/token symbol of the asset you want to receive and click on it.
- You will see a "public address," which you can copy for the sender. Alternatively, the sender can simply scan the QR code to send crypto.
- If there are multiple addresses to pick from, ensure that you confirm the correct network from the sender so that funds won't go missing.
How to Send a Crypto Asset
- Launch your wallet
- Select the asset you want to send
- Choose a network, send it to the recipient's public address, or scan the QR code.
How to access DeFi services via DApp browsers
- Launch your Non-custodial wallet, e.g., Trustwallet.
- Locate the dApp browser icon and click on it.
- Input the website of the DeFi service you want to access
- Select the correct network
Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Decentralized applications are just like your everyday apps, offering similar functions. The difference between a DApp and an App is the "D," which signifies decentralization via blockchain.
DApps can be used to access several DeFi services like a decentralized exchange (DEX).
A DEX allows users access to financial services, like buying and selling cryptocurrency, lending, borrowing, etc. However, unlike a centralized financial system, no single entity controls the network, so DEXs aren't censored by any third party. Instead, instructions are fed into the DEX via smart contracts based on a community agreement.
Smart Contracts
Simply put, a contract is an agreement between two or more parties. Hence, we can refer to smart contracts as a technology that automates the execution of agreements between two parties without needing any third party.
Smart contracts are one of the most critical technologies that keep the blockchain running since it is essential to keep it decentralized.
DeFi Security Practices
- If you see tokens you didn't purchase in your wallet, don't hastily conclude that it's an airdrop, do proper research to be sure it's not a phishing token. If you interact with a phishing token, you may unknowingly agree to a hack that allows the code to spend all your tokens.
- Do your due research before participating in any DeFi product that is heavily shilled to avoid being scammed.
- If a token you intend to invest in has only a few wallets controlling the bulk of a token's circulating supply, it could be a scam. You can check the token distribution info on the associated blockchain explorer.
- Suppose a token isn't volatile and only increases in price sporadically, without any downward movement. In that case, it could be a honeypot scam, where the developers have made people agree to a smart contract that doesn't allow them to sell their tokens.
- Always revoke the access you have granted DeFi services to your wallet.
Crypto/Blockchain Security Practices:
Many hackers try to compromise the DeFi space, disguising several attacks even in smart contracts. Not to worry, below are security protocols that will help you effectively secure yourself, even if you have never written a line of code.
- Ensure that your mnemonic/seed phrase is appropriately backed up. It is not advisable to save your mnemonic phrase digitally or on the internet; instead, it is safer to write them down on paper or something else not connected to the internet.
- If you need a password, ensure that you aren't using a familiar password for your other applications/web services. You can use a password manager service to help you remember one password while using several individual passwords for different websites.
- If you want to hold assets for long without selling, it is best to use a cold wallet.
- When using a custodial wallet, ensure you activate 2-factor authentication.
- Always double-check all SMS and emails to avoid phishing.
- Spread your assets across several wallets.
- Encrypt your devices
- Double-check websites to avoid putting your details on a clone website. It is safer to type the website URL yourself to avoid malicious phishing links.
- Never access your crypto wallet using public WiFi
Types of Scams:
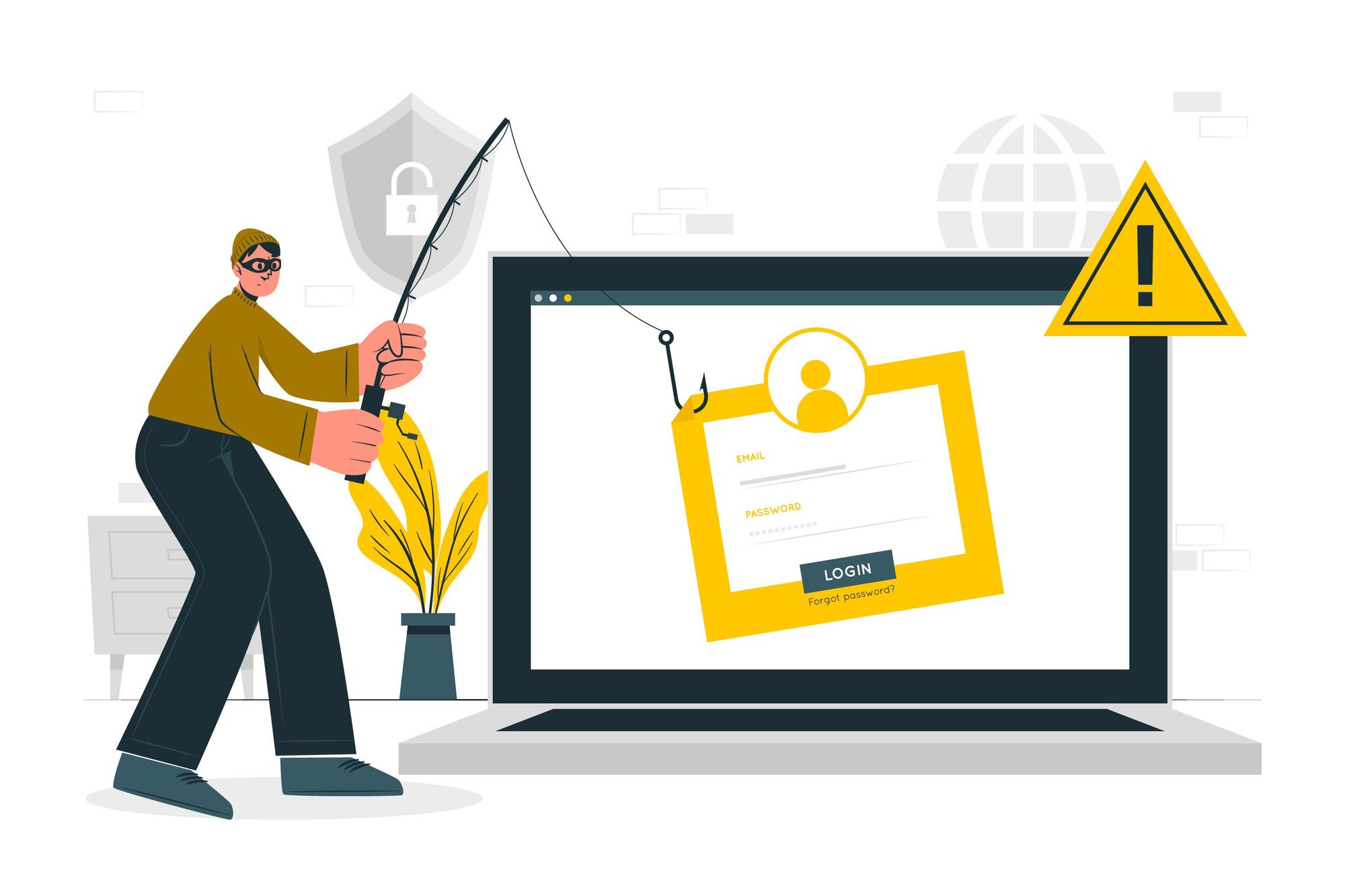

Phishing: Phishing scams have long existed before blockchain and cryptocurrency. It is a cyber attack aimed at maliciously obtaining a victim's details, usually via emails and text messages. These emails and texts typically seem to come from a reputable source, but in a true sense, the attacker is either impersonating a legitimate company or posing as one.
A phishing scam can be simple or elaborate. However, the most common tactic is to send enticing emails with offers that seem "too good to be true." These emails will not directly ask you for your email or password but redirect you to a website (usually a clone of a legitimate company or a fake inexistent company), asking you to log in with your email address and password.
As soon as you enter your email and password, the attacker gets your details via the backend and uses them to gain access to your account, and your money can be wiped in seconds.
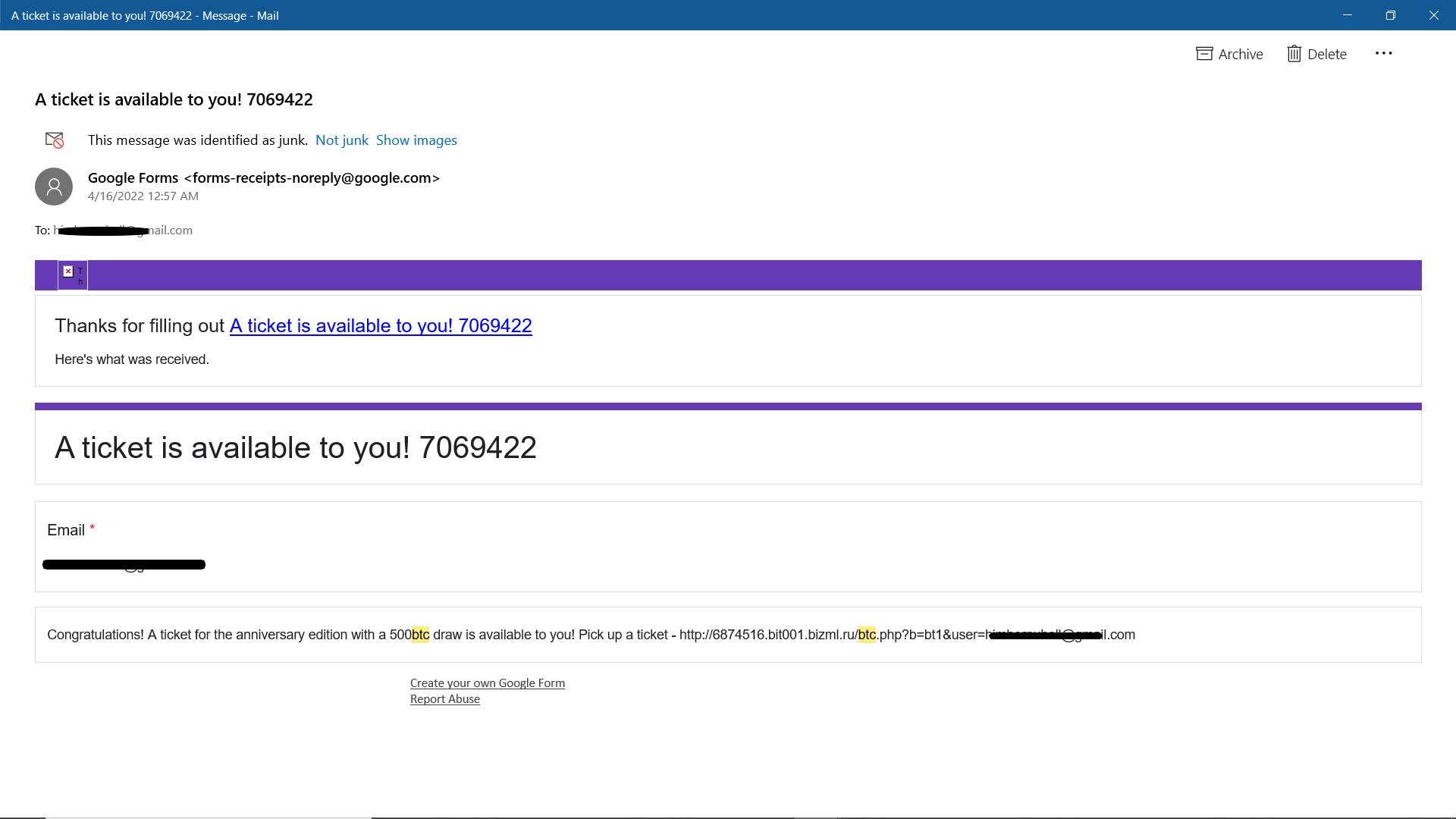
Here is an example. This email promises to add the recipient to a draw of 500 BTC ($20 million), requiring them to sign in to pick a ticket; all the attacker wants is to get the recipients' password and attack them.
Some phishing emails are more sophisticated; they instantly download malware into a device once the victim interacts with the message. Hence, it is essential not to make ANY interaction with messages that appear this way to avoid a massive loss of assets.
Giveaways: Giveaway scams are less sophisticated than Phishing scams, and they should be pretty easy for anyone to identify. Regardless of this, many people fall victim to these scams.
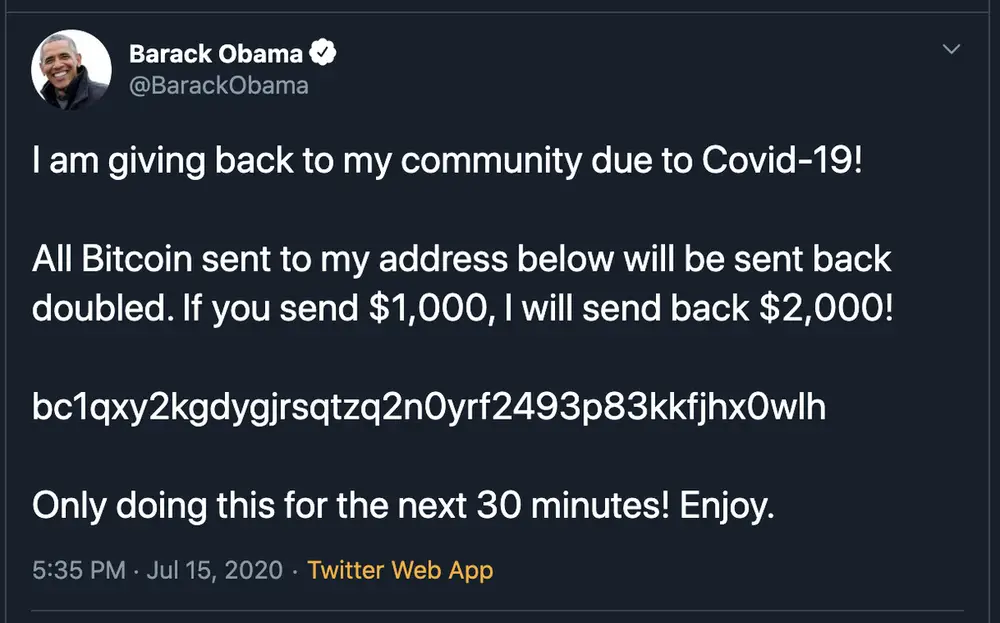
One time, Twitter was unfortunately hacked. The hackers got access to dozens of high-profile accounts, including those of Elon Musk, Jeff Bezos, Bill Gates, Barack Obama, and several other influential people. The impersonators all promised to reward their followers with double the amount they sent in Bitcoin.
There was also the story of a man who famously lost over £400,000 on a giveaway scam by sending 10 BTC to a scammer who posed as Elon Musk.
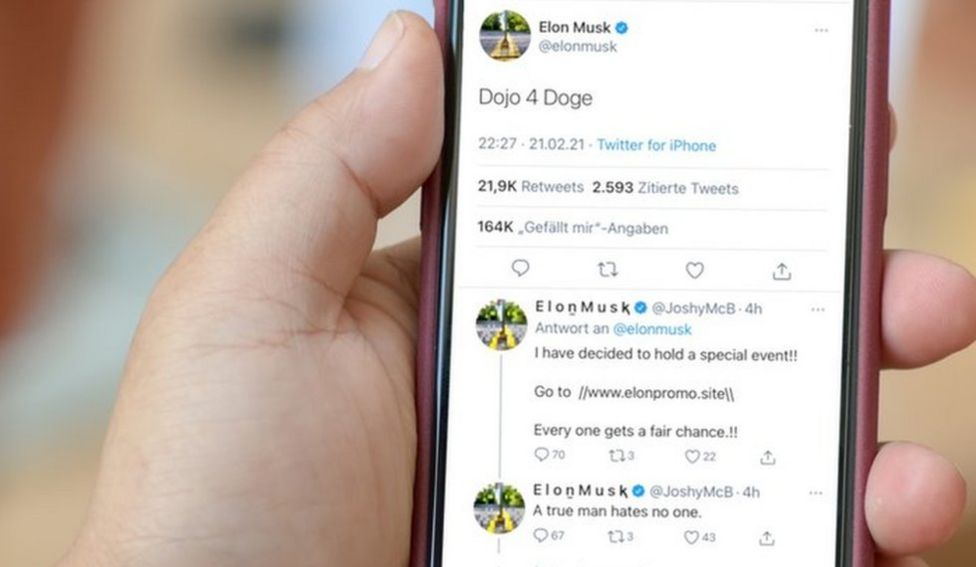
It is essential to be aware that giveaways that require you to send your private key, seed phrase, or any amount of cryptocurrency are scams. The only thing that should be publicly available is your public address.
ICO (fundraiser) scams: Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) are fundraisers to pool funds for a new cryptocurrency project. However, some of these projects aren't genuine, and investors get scammed off their hard-earned money.
Most commonly, after fundraising, the developers of a particular project may leave the herd without any information, possibly getting away with all the tokens distributed. Hence, the investors end up with worthless tokens that may never even make it to the market.
Nearly $700million was lost in ICO scams in 2017; hence, it is essential to secure yourself when investing in ICOs, by strictly adhering to the following practices:
- Read the whitepaper thoroughly to ensure that they have an obvious problem they want to solve.
- Run a plagiarism check on the whitepaper because some projects simply copy tantalizing whitepapers to appear credible.
- Investigate their team members; ensure that they are reputable and can be publicly verified on LinkedIn and/or Twitter. The more reputable the team members are, the less likely it will be a scam.
- Ensure that the Token sale progress is transparent. If it is sketchy or hidden, then you should be wary.
Pump and Dump Schemes: Pump and dump schemes are typical in cryptocurrency. They are famously referred to as "crypto Ponzi schemes" propagated via social media.
They aim to trick unsuspecting and greedy investors into buying a commodity after the perpetrators have initially purchased an enormous amount of said cryptocurrency.
At the end, when the early investors see that there is reduced investment volume, they dump (sell) all their tokens, leading to a heavy price fall, many others will follow suit, and the most recent investors, who have bought lots of tokens will be left with worthless tokens that aren't even worth a cent.
To limit the risk of being caught in Pump and Dump schemes, it is crucial to:
- Invest in tokens only after doing your due diligence - say no to FOMO
- Be careful with meme coins; they are most common for Pump and Dump schemes
- Always read the whitepaper of any token you are investing into, understand the technology behind it, and why the token has value.
- Be wary of coins advertised by crypto influencers; they are most likely pump-and-dump schemes.
- Keep your greed in check when investing in crypto.
Mitigating Losses in Cases of a Security Breach
Of course, prevention is way better and cheaper than cure; however, in cases where your wallet gets hacked, here are some tips to mitigate the losses and avoid future losses.
- If there is anything left in your wallet, transfer it out and keep them in a new wallet.
- Change your old passwords and any other access key linked to the compromised wallet.
- If it happens on a custodial wallet, quickly contact support; you may not recover your assets, but you can help to secure other people.
Final Takeaway
This crypto/blockchain guide aims to provide you with the basic idea of blockchain and cryptocurrency, what it takes to get started, and how you can secure yourself while using several apps.
To get more beginner tips, visit our blog's beginner tips section, where you can get insights on how to adequately navigate the crypto market without a tutor.
If you want to begin your crypto journey without the initial hassles of security and encryption, you should definitely check out the CCTIP Wallet. It is the only wallet that allows you to interact with others in communities, getting free crypto assets from tips and airdrops. So, you can even start your journey from zero!
Join our community of over 25 million registered users, and start your crypto journey with a click.