Comparing Network Fees: Ethereum vs. BSC vs. Polygon vs. Solana
Sometimes, choosing a network to use is not entirely down to you. It all depends on the type of transaction and the token involved. For example, if you want to mint an NFT for a project built on Solana, then you must use the Solana network. However, when trying to send multi-chain assets (like USDT)

If you’ve ever completed as much as one crypto transaction, then you've definitely paid network fees at least once, regardless of whether you paid much attention or not. Simply put, network fees are the charges you pay to network validators for them to pick up your transaction and put it in a valid block of transactions.
These network fees vary across several blockchains, with significant differences in the amounts you pay for your transaction fees to pass through. In this article, we'll take a closer look at four popular blockchain networks - Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain (BSC), Polygon, and Solana - compare their network fees with respect to individual chains’ potential.
That’s not all; we’ll also provide insights on how to eliminate network/gas fees when sending and receiving cryptocurrencies, regardless of the network you use. So, keep reading!
Ethereum
Ethereum is the first blockchain with dApp and smart contract possibilities. Hence, it’s one of the most used networks. In fact, many other blockchains are built to maintain compatibility with Ethereum’s Virtual Machine (EVM) to ensure easy development, as Ethereum has a wide pool of developers constantly working on expanding the possibilities on the network.
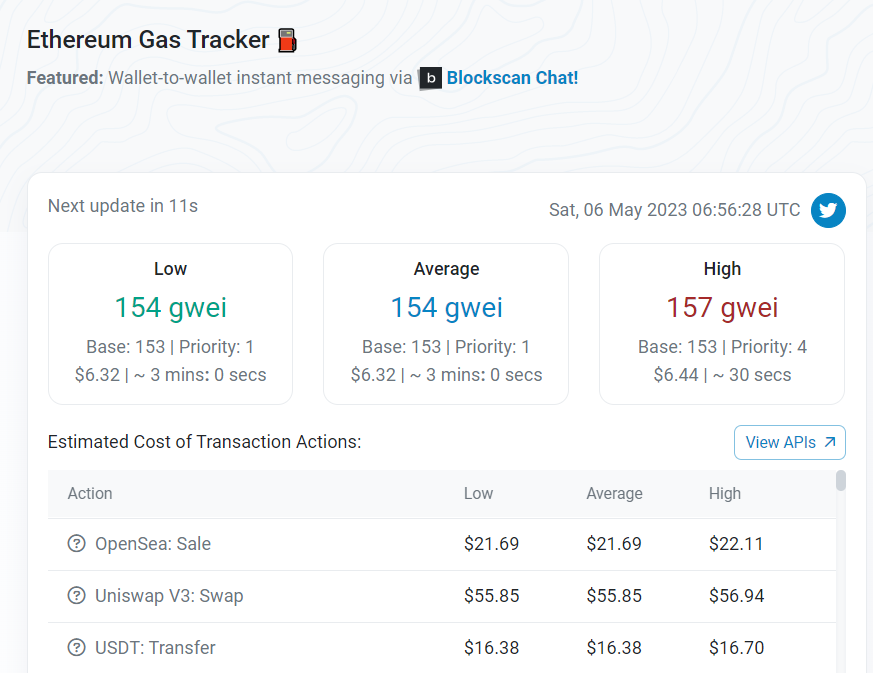
One of the drawbacks of using Ethereum is its high network fees. In times of high congestion, the Ethereum network is unarguably the most expensive to use. However, the network’s reliability, robust developer community, and wide ecosystem make it a landing point for many new blockchain technologies. So, if you prioritize a wide range of use cases, then Ethereum may just be the perfect network for you.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC)
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) is one of the early blockchain networks that was created as a cheaper alternative to Ethereum. It’s also an EVM-based chain, so Ethereum developers could easily build on it.
BSC’s gas fees are only a fraction of Ethereum’s. For example, as of May 6, 2023, Gas fees on Ethereum were over 50 times more expensive than BSC.
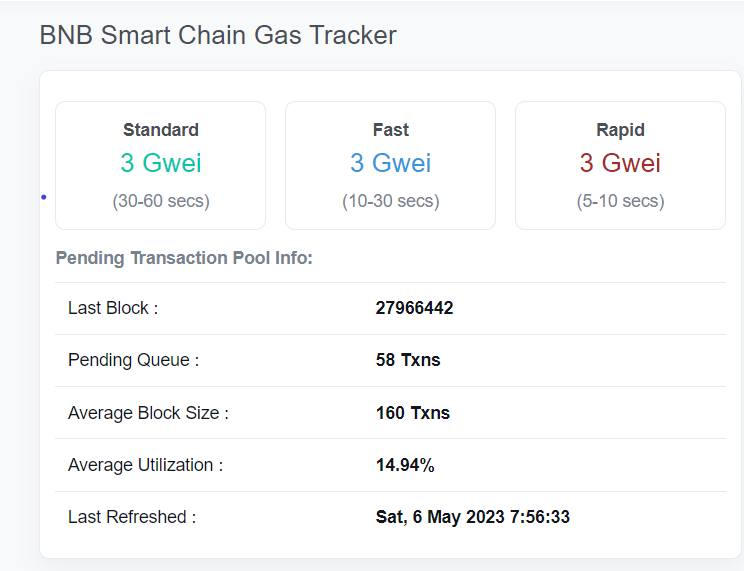
One of the reasons why BSC can offer lower gas fees is because it uses the proof-of-staked-authority (PoSA) consensus mechanism, which is faster and more energy-efficient than Ethereum’s Proof-of-Work consensus (although it’s currently migrating to a cheaper Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism).
Basically, BSC is a lower-budget version of Ethereum with a host of possibilities. However, you may miss out on opportunities to participate in blockchain activities that mainly launch on Ethereum.
Polygon (Matic)
Polygon is a layer-2 scaling solution that comes as a sidechain to Ethereum. It aims to improve the network's scalability and reduce transaction fees by completing and validating transactions on a separate blockchain before merging it with the main chain much later. This allows it to process transactions with much lower gas fees and faster transaction times. In fact, when Ethereum transactions cost tens of dollars in network fees, the Polygon network could process transactions for just a few cents.
Polygon is just one of many Ethereum sidechains, and while it may be one of the best choices for everyday transactions, it has a lower level of adoption for dApps and smart contract transactions since users also consider other Ethereum sidechains like Optimism and Arbitrum.
Solana
Solana is one of the few blockchains that are regarded as “ETH killers.” ETH killers are blockchain networks that aim to beat Ethereum’s performance with higher TPS, cheaper fees, and higher transaction counts.
Solana is one of the cheapest and fastest blockchain networks. Even in times of peak network congestion, Solana transactions barely cost 5 cents. With its unique Proof-of-History (PoH) consensus mechanism, it can confirm transactions very quickly, and transactions hardly spend any time in the mempool before being picked up. Although Solana has experienced a few downtimes in the past, it is one of the most reliable networks for processing transactions and is cheap and fast.
Which Network Is The Best To Use
Sometimes, choosing a network to use is not entirely down to you. It all depends on the type of transaction and the token involved. For example, if you want to mint an NFT for a project built on Solana, then you must use the Solana network.
However, when trying to send multi-chain assets (like USDT) over the blockchain, you can choose the network to use, as long as the receiving party has a wallet on same network. Hence, in a scenario like this, you can choose the cheapest gas fees and go for it.
In all, you can avoid paying fees for sending and receiving cryptocurrencies and NFTs, regardless of blockchain network, when you transact with Cwallet.
Cwallet allows all users to send cryptocurrencies to other Cwallet users at absolutely no cost. All you need to do is create an account, and you will be issued a unique Cwallet ID. With this ID, you can transact for free without needing to worry about expensive gas fees!
Cwallet is compatible with 800+ tokens and 50+ blockchains, so you have unlimited options when transacting with Cwallet.
So why delay? Try out Cwallet today, and say goodbye to network fees!