HOW TO TRADE ON A SPOT MARKET?
As a newbie in crypto, it is very likely that your first crypto purchase will be done on a centralized exchange, and to efficiently do that, you need to understand the dynamics of a spot market and how to navigate through your first trade.

Spot Trading is a common term in crypto communities. If you are a crypto twitter regular or an active Redditor on crypto discussions, you’d see phrases like “buy on spot.” As a newbie in crypto, it is very likely that your first crypto purchase will be done on a centralized exchange, and to efficiently do that, you need to understand the dynamics of a spot market and how to navigate through your first trade.
What is A Spot Market?
The spot market facilitates the instantaneous buying and selling of financial instruments, such as cryptocurrencies, commodities, fiat currencies, forex, stocks, bonds, securities, etc.
Yes, the spot market is limited to cryptocurrency. As long as the transaction is delivered immediately and the cash is paid upfront, it is known as a spot market. So, if you have experience trading stocks, you most likely are not new to spot trading.
How Does Spot Trading Work in Cryptocurrency?
Since the spot market facilitates immediate delivery of assets to the purchaser, traders often engage in spot trading to buy assets quickly and sell when they have made enough profits.
Unlike non-spot trades, where specific agreements must be reached before asset delivery, spot trades are pretty fast, involves low spreads, and traders can open/close positions “on the spot.” Hence, the name “spot trading.”
Crypto assets are very volatile, and prices can dramatically drop in minutes or even seconds. Hence, spot trading is essential, especially for day traders and scalpers, to lock in their profits and not lose their gains to volatile downward price movements.
Spot Trading can be done over the counter or via crypto exchanges.
· Over The Counter (OTC): An OTC market is unregulated peer-to-peer trading without the involvement of a third party (whether an escrow, broker, automated market maker, or a liquidity pool). It is totally traded “offline.” For example, if you want to buy $5 worth of coins, and your friend wants to sell that exact unit, both parties agree on the rates and terms, and the trade is completed instantly (on the spot).
Obviously, the downside of OTC trading is that it requires some level of trust to ensure that you won’t get duped. However, the upside is that you can make small transactions without being limited by exchanges or without being asked to pay huge transaction fees.
· Spot Trading Via Exchanges: Unlike OTC trades, Spot trading via exchanges is regulated. It works differently with Centralized Exchanges and Decentralized Exchanges
When carrying out a spot trade via a DEX, transactions are automatically executed by an automated market maker (AMM). An AMM is a protocol that determines asset prices via an algorithm. Hence, rather than matching a buyer with a seller, the algorithm automatically calculates the price via a predetermined formula and instantly completes the transaction with the aid of a liquidity pool. There are no order types with DEXs; all trades are executed similarly via smart contracts.
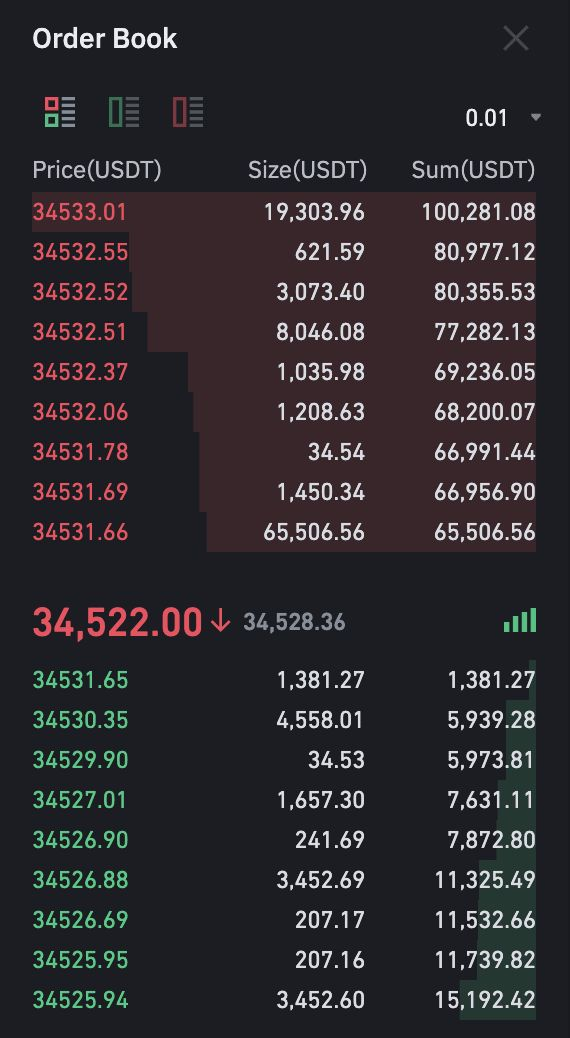
Conversely, Centralized Exchanges (CEXs) typically use order books to match buyers and sellers. The order book contains a list of buy and sell orders and instantly matches a corresponding buy order to a sell order for immediate delivery.
Below is an example of an order book, with the buy orders in green and the sell orders in red.
Spot Trading on CEXs is somewhat dynamic when compared with DEXs. Below are five standard order types when carrying out a spot trade via a CEX.
Market Order: A market order executes buy and sell orders instantly, automatically fulfilling the order at the immediately available market price. In this, the buyer/seller has no control over the trade, and if an instant surge or drop in price occurs, the buyer/seller may get more or less than what they initially bargained for.
For example, if you place a market order to purchase $10 worth of coin X at 0.01$ (totaling 1,000 units), an instant surge happens, raising the unit price to $0.05$ while you confirm your order. As a result, your order will proceed; however, your $10 will only be able to purchase 200 units of the said coin.
Market prices rarely experience a rapid surge/dip within seconds of an order completion; however, it is a possibility that must be considered since heavily volatile movements can happen within seconds.
Stop Order: A stop order is created to cut losses short while trading on the spot market. It can also be called a stop-loss order.
For example, if coin X is trading at $5.00, and a trader wants to purchase but wants to simultaneously mitigate possible losses, they can buy with a stop order. Hence, if the trader cannot afford to lose more than 30% of their investment, they can place a stop-loss at $3.50. If the price falls to $3.50, the position is automatically closed, and the asset is sold.
However, if cases where prices are rapidly falling, the demand will become way lower than the supply; hence, the system may be unable to instantly match a seller with a buyer, and the price may fall even lower than $3.50 (or whatever stop order price is set).
Limit Order: Limit orders provide investors the leverage to put a limit on the price at which they want to buy/sell a crypto asset. Unlike market orders, limit orders help traders hedge against volatility.
For example, if coin X is trading at $0.20, a trader can place a buy limit order to purchase at $0.18. Hence, the trade will not execute at any price higher than $0.18. This helps to mitigate the risks associated with market orders, but unlike market others, it could take a little more time for the order to get filled up.
Stop Limit Order: A stop limit is an improvement over the limit order. Ordinarily, with a limit order, you can only set a buy limit below the current price. However, you can set a buy-stop limit above or below the current price with a stop-limit order.
Recall that a limit order will NOT execute above the market price; hence, you may miss out on the purchase entirely, but you can set a limit above or below the current market price with a stop-limit order.
For example, if a coin is trading at $5.00, and you want to buy; however, you want to be sure that the market is indeed in a positive trend before placing the order, say if the price crosses $8.00, your bias will be confirmed that the trend is positive. Hence, you can use a stop-limit order if you want to place a buy order but want more upward movement first.
The stop-limit order requires you to set a stop price and a limit price. Hence, the order automatically becomes a limit order if the stop price is reached. In this case, you can set your stop price at $8.10 and your limit price at $8.00. So, your buy order can be executed at a higher price than the current market price.
N.B.: If the stop price isn’t reached, the limit price won’t be activated.
One Order cancels another Order (OCO): An OCO order is an excellent way to set two limits on buying/selling a coin. An OCO combines a stop-limit order and a limit order in one; however, only one of both can be executed. So, if either order gets filled, the other will automatically be canceled. Below is an example.
If you want to purchase some units of a coin trading at $5.00, based on your analysis, you have set two action levels for the asset’s movement. You believe that the coin will pump higher from $8.00 or drop to $3.50 before pumping higher. As a result, you can set a Limit order at $3.50 and a stop-limit order at $8.00.
If the price goes down to $3.50, the limit order will be filled first, and the stop limit will be invalidated. Similarly, if the price goes up to $8.00, the stop-limit order will be served, and the limit order will be invalidated.
This allows traders to execute versatile trades in line with their technical analyses, support, and resistance levels.
How To Execute A Spot Trade On any Centralized Exchange

Executing a spot trade can be done in five simple steps:
- Select a preferred CEX and create an account.
- Complete your KYC verification, and familiarize yourself with trading rules and fees.
- Figure out how to load money into your account; typically, if you are trading a BTC/USDT pair, you will need some USDT to buy BTC. So, you may need to get some USDT via a credit card or the platform's p2p market.
- Locate the intended trading pair.
- Select your preferred order type as listed above, and place an order.
Benefits of Spot Trading:
- Placing orders in a spot market is very easy, requiring almost no expertise. A beginner can easily estimate profit levels as well as risk/reward.
- Spot Trading on CEXs provides you several options that help you execute your trade without sitting all day monitoring them.
- When trading on CEXs, pricing is transparent, based on the demand and supply in the order book.
Disadvantages of Spot Trading
- OTC orders are susceptible to fraud
- There is no room for multiple profits as it would be in a derivatives market.
- Depending on the order placed, spot markets can expose you to volatility risks, making you buy or sell at a less profitable price.
Final Takeaway
We hope you have gained insights into trading pairs on a spot market easily and fast. We urge you to try your hands on any CEX of your choice and buy a few crypto assets.
You can also explore more options with your asset using the CCTIP wallet; all you need to do is download the application and create an account. Then, you can enjoy the unique features of the CCTIP wallet, including tips, airdrop games, and giveaways.
Stay updated with the CCTIP blog and join our community for frequent updates and information.